Potential Due to a Point Charge
Potential Due to a Point Charge: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Graph of Electric Potential Due to Point Charge and Electric Potential due to a Point Charge at a Point
Important Questions on Potential Due to a Point Charge
Charges , and are placed at three corners A, B and C respectively of a square ABCD of side . Find what charge must be placed at the fourth corner so that the total potential at the centre of the square is zero.
An electric dipole is placed as shown in the figure.
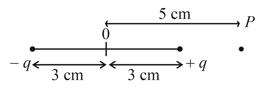
The electric potential (in ) at point due to the dipole is (=permittivity of free space and )
Electric potential at a point due to a point charge of is . The distance of from the point charge is:
(Assume, )
Find the distance from a point charge of magnitude , where electric potential is
The electric potential on the surface of a sphere of radius due to a charge is . The intensity of electric field on the surface of the sphere in
Around a stationary charge of , another charge is taken once round a circle of radius . The amount of work done in joule is
Two charges each of are placed at distance of calculate the potential at the midpoint if dielectric constant of the medium is .
Mark the correct statement(s) for the situation shown:
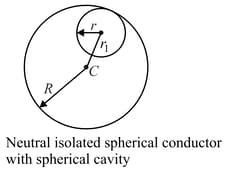
Mark the correct statement(s) for the situation shown:
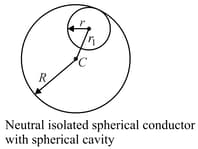
The potential due to charged spherical conducting shell of radius at point distant from centre is . The potential on the surface of spherical shell is
Two charges and are placed at two vertices of equilateral triangle of side . The potential at third vertex of the triangle is
ABCD is a square of side point charges are placed at corners A, B and C respectively. Calculate the amount of work done required in transferring a charge of from D to the point of intersection of diagonals.
The electric field due to a point charge on another is directly proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Write the equation of electric field due to a point charge. Also name the terms in it.
Electric potential due to point charge in air is expressed as as . i.e for to potential varies
The graph of variation of potential due to point charge vs distance is said to be symmetric
Electric potential due to point charge in air is expressed as as . i.e for to potential varies
Which of the follow graph is correct for potential due to point charge at any point versus distance as shown in figure.
The graph of variation of potential due to point charge vs distance is said to be _____ symmetric
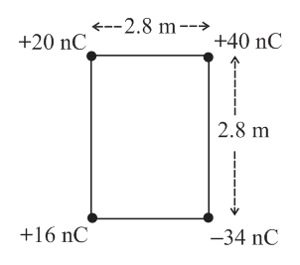
Four point-charges are placed at the vertices of a square of side as shown in the figure. Find the electric potential at the centre of the square.